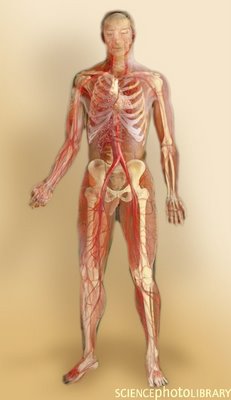
Immune system
This image shows the immune system. The immune system guards against invading organisms that may cause infection or disease. The the first line of defence is the skin and mucous membranes. The second line of defence is composed of white blood cells. White blood cells circulate around the blood system and destroy microorganisms that have penetrated the mechanical barriers of the body.

The immune system response
This image shows the immune system's response to a thorn (brown, centre left) that has pierced the skin. Bacteria (dark red) are ingested and destroyed by white blood cells (pale blue, lower left).

White blood cell
This is an electron micrograph of a type of white blood cell called a lymphocyte. Lymphocytes are divided into two main types of cell: T-cells or B-cells.
T-cells mature in the thymus and fight antigens by engulfing or swallowing them. NK-cells (natural killer cells) are a type of T-cell and seek out antigens and kill them.
B-cells mature in bone marrow and produce antibodies to destroy antigens. Antibodies stick to viruses and bacteria and slow them down. T-cells can then catch and destroy them.
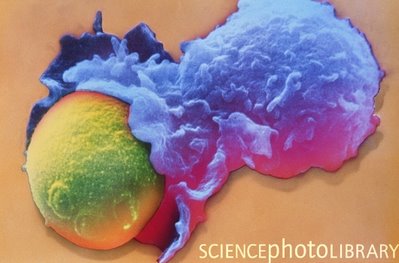
T-Cell
An electron micro-graph image of a T-cell (blue) destroying an antigen (green). The antigen is swallowed up and digested.
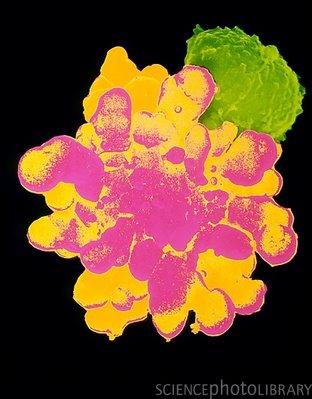
NK killer cell
An Electron micrograph image of a Natural Killer cell (green) attacking a large cancer tumour cell (pink & yellow).
This video from discovering psychology investigates the relationship between stress and the immune system. It looks at mind/body interactions and their relationships to disease and the immune system. Scroll down the screen and find video 4.
Video 4: Cognition and the immune system











No comments:
Post a Comment